Learning Python
Python
Has Python caught
your attention? If that's so, have you once questioned if learning is
challenging? I'll explain what Python is in this blog and why studying it could
be beneficial for you.
Introduction
Python is a high-level, interpreted computer
programming language that's popular across many computer technology development
fields, including web development, scientific computing, data analysis,
artificial intelligence, and more. From its first publication by Guido van
Rossum in 1991, it has grown to be among the most widely used programming
languages worldwide, especially popular among individuals learning and familiarizing
themselves with the world of computer programming. Python is straightforward to
learn and use for novices because of its understandable syntax. Programming
styles including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming are
all supported, making it as efficient as other high level programming languages
like java. For a wide range of activities, including working with files,
networking, web development, and more, Python includes a sizable standard
library that offers a comprehensive set of modules and tools. Python is an
interpreted language, meaning it doesn't require compilation since the interpreter
runs the code automatically. As a result, programs can be developed and tested
efficiently without having to worry about linking or compiling. Python is a
robust language and can be implemented on multiple operating systems, namely
Windows, Linux, and macOS, increasing is
Why learn Python?
Python
is the ideal choice for your first programming language, and I'll go through
some of the factors below that makes it so user-friendly;
1. Simple and Easy to Understand
Syntax: Python offers a simple and easy-to-read syntax, making it
straightforward to learn and understand for newcomers. The code is expressed in
statements that resemble English and are simple to read and write.
2. Huge Developer Community:
Python has a massive developer community that adds to its libraries,
frameworks, and tools. This community offers excellent learning materials,
documentation, and support for new as well as experienced developers. The
official Python repository contains around 500,000 projects.
3. Flexibility: Python is a
flexible language that can be applied in a variety of contexts. It has been
applied to Data analysis and visualization, machine learning, scientific
computing, web development, Desktop application development, automation,
and scripting.
4. Python has an extensive
number of modules and frameworks that makes the development process easier.
Developing web apps rapidly is made simple by well-known frameworks like
Django, Flask, and Pyramid.
5. Cross-Platform: Python may be
implemented on a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and
macOS. Python programming is adaptable and simple to use across several
operating systems.
Python Syntax
Python was created
as a programming language that is simple to read and write. Its layout is
aesthetically clean and frequently replaces punctuation with English terms. It
does not need curly brackets to separate blocks, whereas many other programming
languages use any kind of punctuation.
Statements:
The majority of
statements in Python are identical with those in other programming languages.
1.
Assignment
statement: Assigns a value to a variable. Example: a = 5
2. Conditional statements are used to execute
different actions based on different conditions. The most common conditional
statements in Python are if, if-else, and if-elif-else statements.
3. Loop statement: With a loop, a block of code is
repeated until a condition is satisfied, a certain number of times.
4. Import statement: A module or a single function or
class from a module is imported using the import statement.
5. Print statement: Statements that print the value or
a string to the console
6. Exception statement: In a try-catch block, the code within the try
block is executed, and if an exception occurs during the execution, the catch
block is executed. The catch block contains the code that handles the
exception, and it can log the error message, provide an alternative code to
handle the exception or notify the user.
Variables and
objects:
Variables are
used to store values that may be changed and utilized during the course of
the program. We can assign values to variables simply by
assignment operations that are ‘=’. Their values can be changed during the execution
of the program. Python is dynamically typed which means it can detect the type
of variable it is. Example: a=3. In python, values are stored in objects. Below
are some of the most commonly used objects and their class types.
|
Object Type |
Type class name |
Description |
Example |
|
Integer |
Int |
Integer value, 32 bit |
b=2 |
|
Float |
Float |
Double precision floating point number, 64 bit |
b=45.76 |
|
Complex |
Complex |
Complex number |
b=5+65j |
|
Character |
Chr |
Single byte character |
b=’r’ |
|
String |
Str |
List of characters, Text |
B=’tredt’ |
Datatypes:
There are numerous
frequently used data types in Python. They consist of Booleans, strings,
floating-point numbers, integers, floats, and lists.
Whole numbers such
as 999, 8, and -154 are examples of integers. The "int" data type in
Python is used to represent them.
As examples of
decimal numbers, consider 36.1445, 7892.5, and -0.675. The "float"
data type in Python is used to represent them.
Character sequences
known as strings include "Hello, World!" and "Python is
wonderful." The "str" data type in Python is used to represent
them.
In Python, the
"True" and "False" keywords stand in for booleans, which
are true or false values.
Collections of values,
which may be of multiple data kinds, are called lists. The "list"
data type in Python is used to represent them.
Expressions:
Expressions that
evaluate numeric values are known as numerical expressions in Python. These
expressions may include numeric values, variables, and arithmetic operators. Some
of the expressions are +. - *, / etc.
Functions:
In a program,
functions are reusable chunks of code that may be used repeatedly. Following
the function name and any parameters the function accepts, they are declared
using the "def" keyword.
Example: def add_numbers
(x, y):
return x + y
A very simple
example to calculate area and perimeter of rectangle using functions.
Some
Programming Examples:
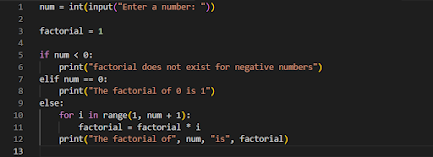
Program to find factorial of a number:
Python
packages:
A package contains all the files you need for a module. Modules are
Python
code libraries you can include in your project. Since Python is open source,
you can find thousands of Python Packages that you can install and use in your
Python programs. You can use a Python Distribution like Anaconda Distribution
to download and install many common Python Packages as mentioned previously.
The command-line utility known as PIP, or "Package Installer for
Python," is used to manage and install Python packages. We can
simply install, update, and delete packages from the Python Package
Index or other package indexes using this package manager, which is the
industry standard for Python.
Around 250,000 Python packages are available in the PIP repository,
where you may search for and install programs. To make it simple for other
developers to install the necessary packages for your project, you can also
declare dependencies for your Python projects.
Conclusion
Python is a strong language of programming used for a variety of tasks,
including scientific computing, web development, desktop
applications. You may start writing your own Python programs and
uncovering the tons of features that come with this popular language by knowing
the underlying principles of Programming skills.

Comments
Post a Comment